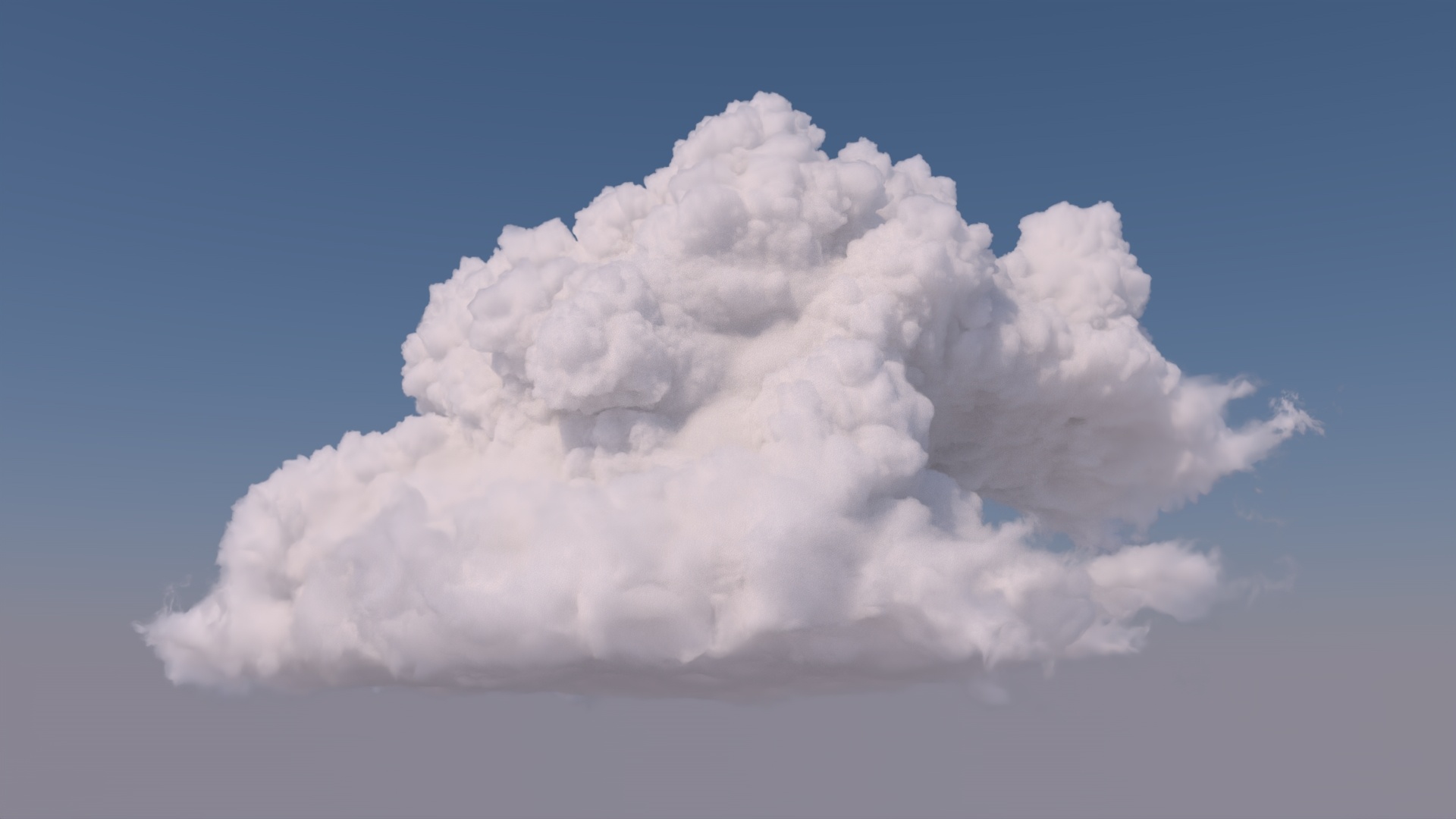
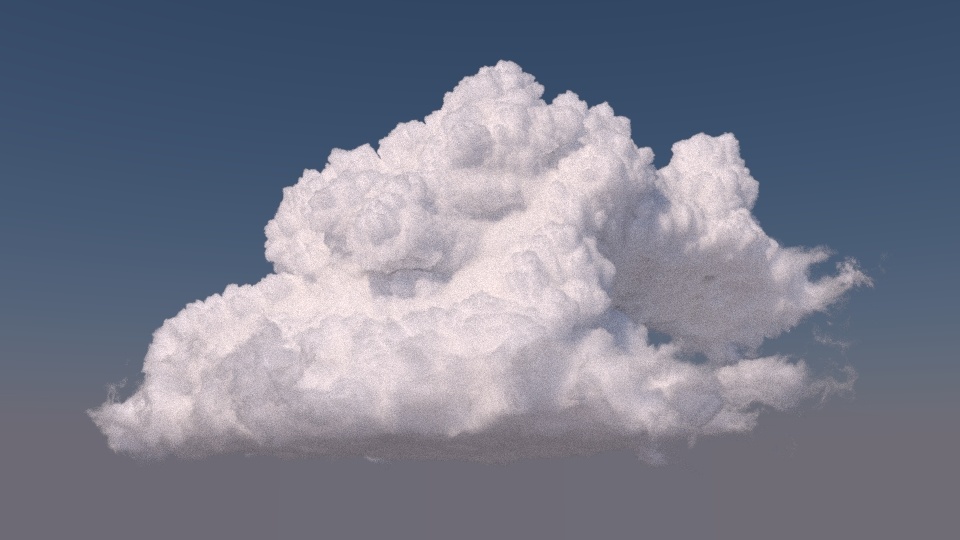
The Moana Cloud asset rendered using the Aggregate Volumes workflow. OpenVDB Asset courtesy of Walt Disney Animation. CC BY-SA 3.0 License.
When rendering clouds with the Aggregate Volumes workflow, there are a number of key settings that you can adjust to control the look of a cloud. All images on this page were rendered using a scene set up in RfM. Instructions for setting up the scene can be found in the Scene Setup sectionThis document outlines aggregate volume controls in the context of rendering clouds.
Volume Settings
Max Path Length
...
| Note |
|---|
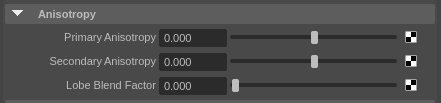
Enabling anisotropy will introduce additional noise to your render. Higher values of anisotropy will introduce more noise. |
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Scene Setup
This section covers how the scene used above was set up in RfM.
...
First, create an OpenVDBVisualize object from the RenderMan shelf tab.
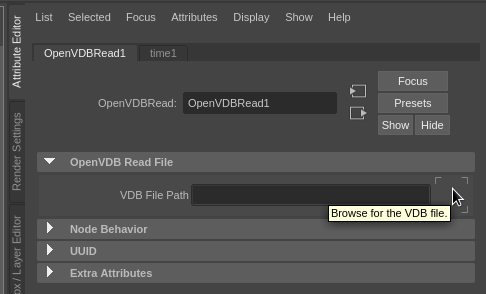
Next, select the VDB file you want to use in the OpenVDBRead settings in the attribute editor (the quarter or eighth resolution versions of the Moana cloud are fine for nowCloud work well for tweaking settings).
Now, you should be able to see a wireframe of the leaf nodes and tiles in the viewport (you may have to zoom out to see the whole cloud). Next, select the OpenVDBVisualize object in the outliner and open the OpenVDBVisualize settings in the attribute editor. Here, we want to you should rotate the volume so that the top of the cloud is in the +Z direction. So, add a 90 degree rotation along the X-axis.
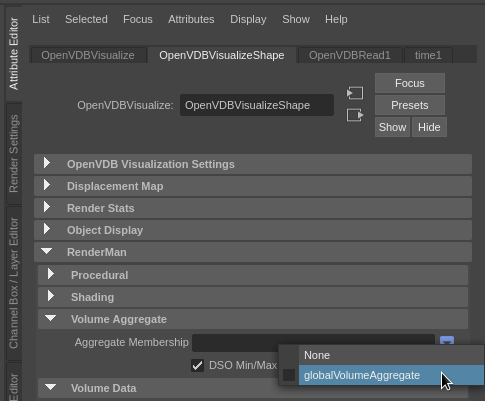
The last thing we want you need to do in the volume settings is add the volume to a volume aggregate. The globalVolumeAggregate is created automatically, so under the OpenVDBVisualizeShape settings, in RenderMan > Volume Aggregate, set the Aggregate Membership to "globalVolumeAggregate".
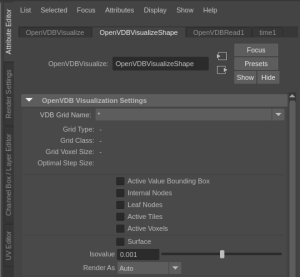
You may also want to disable the visualization of leaf nodes and active tiles, which is under the OpenVDB Visualization Settings.
Volume Shader Settings
In the shader settings, you can also adjust the anisotropy settings under the Anisotropy area. By default, anisotropy is off.
Light Setup
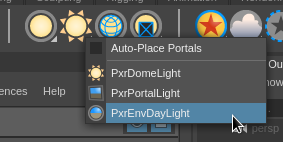
For the light setup, we will use a PxrEnvDayLight. So, the first step in the lighting setup is creating a PxrEnvDayLight from the Renderman tab of the shelf.
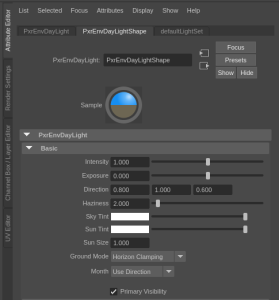
Next, you can adjust the light direction under the PxrEnvDayLightShape tab of the attribut attribute editor either using the Month/Day/Year/Hour (the default method in RfM) or using the Direction control by selecting Month > Use Direction. For To replicate the scene used in this tutorial, we use the direction controls and set the direction to 0.8, 1.0, 0.6. I also found it useful to You should also change the "Ground Mode" from "Legacy" to "Horizon Clamping".
The other defaults provide a good starting point so you can leave them unchanged for now. This is also where you will adjust your MSApprox settings (under Multi-Scatter Approx). It can be quite hard to predict how MSApprox will affect the render, so you should wait to adjust these settings until after the render is set up completely.
...
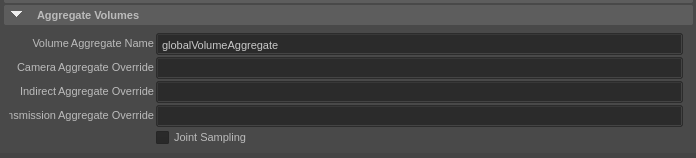
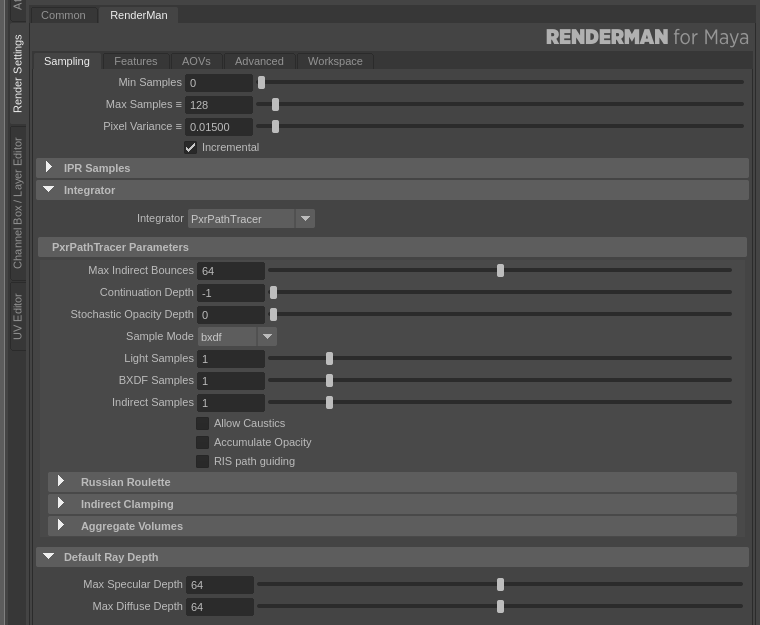
The last thing we need to tweak before we see our cloud rendered is the Render Settings. So, open the Render Settings and select the RenderMan tab. The first thing you should change is under the "Aggregate Volumes" tab. For "Volume Aggregate Name", enter "globalVolumeAggregate" (this is the volume aggregate we added our cloud to before).
Once you set the volume aggregate name, you should see the cloud if you start a render (either in the viewport or externally in "it"), but it still won't look quite right. To give the cloud the correct appearance, we need to adjust the number of bounces. First, under "Default Ray Depth", adjust both the "Max Specular Depth" and "Max Diffuse Depth" to much higher values (e.g. no less than 32), and under "PxrPathTracer Parameters", set "Max Indirect Bounces" to that same number.
Multi-Scatter Approx
...
Now that everything is set, you can kick off a render and see the final image, which should look something like this: