...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
For screens with a high DPI you may find the text is hard to read. You can change this manually. Look for the file here: $RMANTREE/lib/Resources/stylesheets/it.qss This acts like a Cascading Style Sheet for "it". You can alter the text size using this section:
Since we don't recommend altering shipped files, you may put a copy of your new .qss file in your custom directory defined by the environment variable: RMS_SCRIPT_PATHS |
Catalog
This window shows all the images and renders that are stored in the current "it" session. Multiple catalogs can be used, each storing their own images. To create a new catalog, go to File->New Catalog.
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
'it" can interactively denoise beauty renders for preview purposes using Nvidia's AI Denoising solution. You can choose this in the View menu or press N on the keyboard to toggle this on and off. This requires the latest Nvidia drivers (391.89 as of this writing) and an Nvidia GPU on the system that is reasonably modern (Minimum is Kepler, newer cards will perform significantly better). Images that are more converged (has more samples) will achieve better quality. Insufficient convergence will resemble a watercolor or "painterly" style image.
This feature is meant for interactive preview rendering only, it it not designed for final renders or animation. AI Denoise only operates correctly on the beauty (Ci) and not on AOVs. To correctly view AOVs, toggle the denoiser off or you will see artifacts. The final EXR output is unaffected by the denoiser. Use the Snapshot feature of "it" to save the denoised Beauty instead (see below this entry).
| Info |
|---|
Denoising options want statistically independent pixels, this means you should either manually provide the rendering option for "Importance Sample Filtering" for pixels or select the Denoise option in the appropriate bridge product that will enforce the Importance Sample Filter for images. If this is not enabled then no change will be seen when using the Optix Denoiser. |
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
From the Commands window you can choose to Snapshot an image. This makes a quick copy of either a completed render or an (in-progress) interactive session. There is also an option for No AOVs should you just need to capture the beauty render. This is useful for interactive sessions where you want to save how a current scene looks before you make a change and then compare them. This places the snapshot next in the Catalog list. To save an image that is using the Nvidia AI Denoiser, you must use Snapshot as an export will only save the underlying raw image. You must also have Catalog Menu > Burn In Mapping On Save selected.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
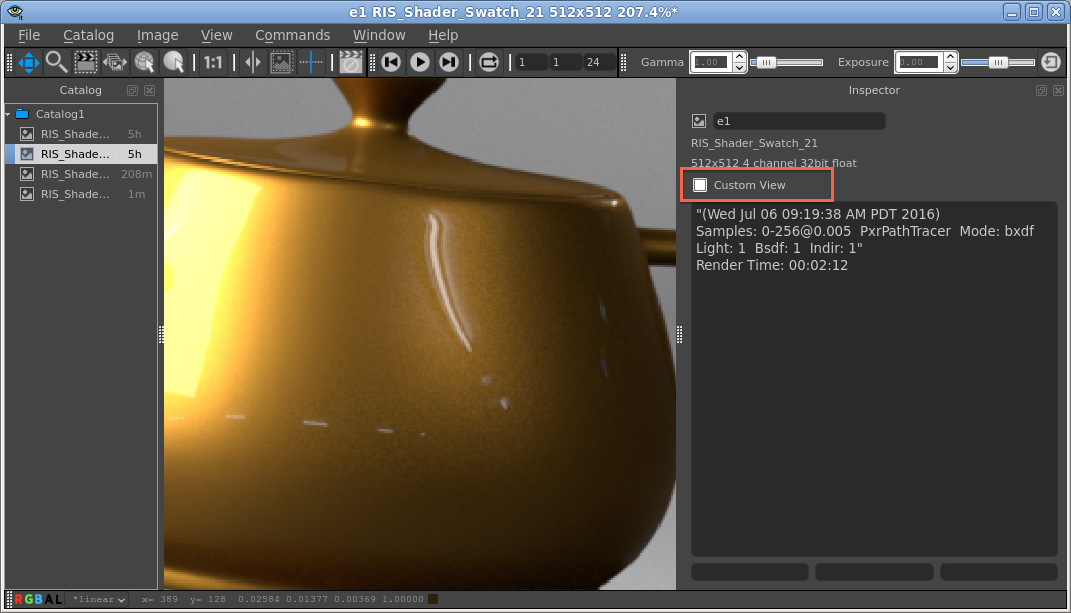
Views in "it" are a combination of zooms, pans, pixel aspect ratio and view mappings. By default all images in a catalog share a view. This is convenient when you want to step through a shot that you've rendered to "it" (hot key PageUp/PageDown). When you zoom in and step to the next frame in the shot the zoom and pan remain the same. However, sometimes you'd like to be zoomed way in on one image to look at some feature and then flip between that and a zoomed out image. "it" accommodates this with Custom View. When you turn on Custom View for an image, that image then has its own zoom and pan, independent of the other images in a Catalog. Custom Views are saved if/when the Session (or Catalog) is saved.
Pixel aspect ratio is useful when working on projects that generate non-square imagery. One example of this is the film format Cinemascope. In some pipelines you might decide to keep your digital files in a format where a pixel is half the size in the horizontal direction than the vertical. 'it' allows you to specify this in the view so that on your monitor images look normal. This menu is fully configurable from your it.ini file including the names on the menu and the aspect ratio of the pixels. You may also attach short cut keys to different aspect ratios even if you customize this menu.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
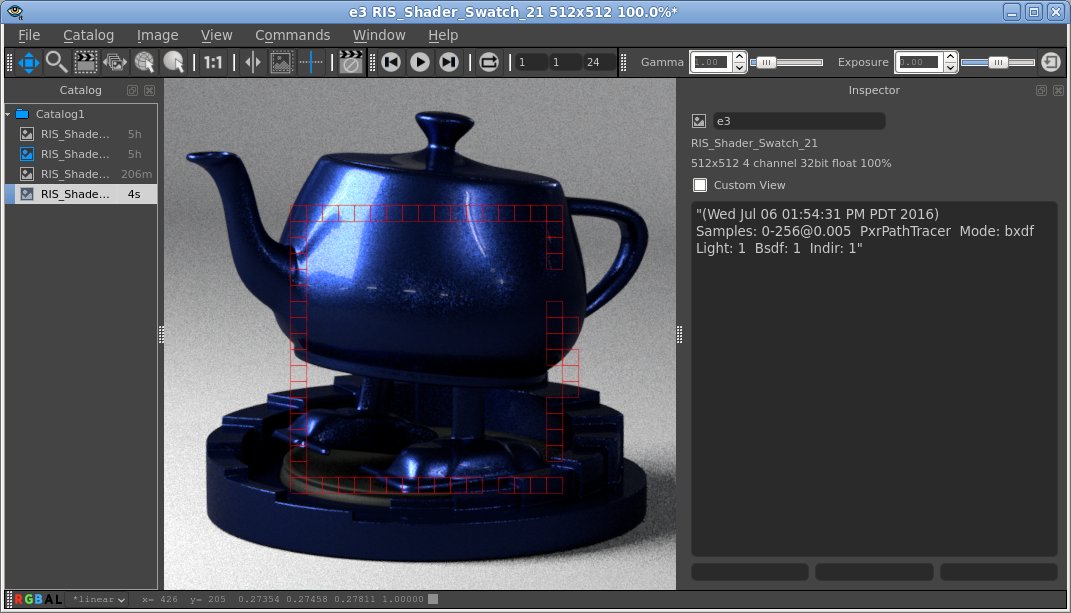
When 'it' is being used as the destination for a render it will display a rectangle around each bucket as it arrives. The indicator will fade over a few seconds. This is useful when an image in being refined as it is sometimes difficult to see what part of the image the renderer is working on. This feature can be toggled on and off and the color of the rectangle can be altered in the preference dialog.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
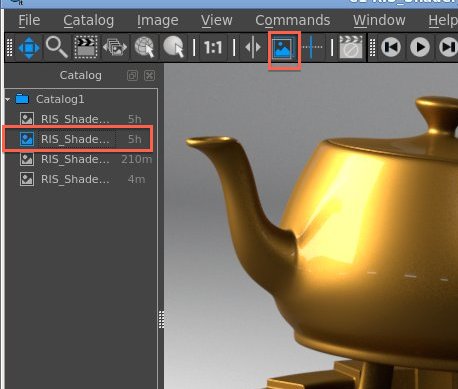
Any one image in a Catalog can be set to be the Background image. When you then select other entries in that Catalog, the displayed image is the result of compositing the selected image over the nominated background. To toggle the current image to be a background image, use Image->Toggle Background. The icon next to the image in the Catalog will then light up. See Working With Background Images.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The remap menu shows the color space that your image is in. Typically this would be linear for rendered images and sRGB for 8 bit image files. By default "it" chooses the image space of the image and when it does this the image space is preceded by a *. You can use the menu to override "it"'s choice (the * indicator will go away)
"it" supports view mapping output images to accommodate your workflow of choice using the OpenColorIO system. Your view mapping defaults can be set for images rendered to "it" as your framebuffer (regardless of bit depth) or for imported images (with different mapping for different types, if necessary).
There are several important things to remember about remapping:
Remapping is applied only for viewing files. It is not burned in. See Burn Mapping On Save preference.
Images rendered via RenderMan are, by default, in linear space, unless an exposure is applied to the output (which can be done in RfM via the Output Settings tab of the RenderMan controls).
If you do apply an exposure to your output, be sure to make the proper adjustment to the default image mapping for rendered images.
The OpenColorIO setup can be changed via your it.ini, though, as always, we strongly recommend making the changes in a site-specific surrogate ini file, referenced via RMS_SCRIPT_PATHS. "it" will also use the environment variable OCIO if it is set to find the OpenColorIO config file.
A special entry on the remap menu is the Shadow Map option, which is useful for viewing shadow map files. These files can have huge ranges that are well beyond zero to one, so the traditional way to display these has been to rescale the min and max values to zero and about 0.9, and then invert them with (1 - val).
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sequences are for when you've rendered a shot or perhaps a wedge of parameters to a shader and now you would like to see them all played as a sequence. The Sequence toobar has the controls for starting and stopping playback and the frame range controls. "it" will either play the whole catelog or you can open a set of images on disks as one element (called a "sequence"). There is also a "scrub" mouse tool which when activated lets you move through a sequence by dragging with the left mouse button in a horizontal direction.
An image sequence can be created by opening multiple files on disk in a directory, use File->Open Sequence instead of File->Open Image. "it" will discern which files belong to the sequence; and the frame range will appear in the Sequence toolbar.
Sequences are low tech in that they don't provide a way to save or load movies, and the entire "movie" is held in RAM. "it" places a cap on the number of images it will hold in RAM so for smooth playback you will need to set that cap (Image Cache Size) to at least the number of frames in your sequence.
...