This is a displacement plugin that displaces the surface point P in the current space (typically object space). It supports both scalar and vector inputs. It sums up all the connected scalar and vector inputs before it does the actual displacement.
...
| Note |
|---|
You need to set your displacement bound in order to see displacement. Displacement bound is automatically set in RenderMan For Maya. For performance reasons one is not always set by default. Use small values at first, if you have clipping, increase the value slowly. |
| Info |
|---|
To match Displacement from previous version of RenderMan, the following conversion may be of use: To get a similar tessellation level, using a shading rate (deprecated) value of X would translate in using a micropolygonlength value of sqrt(X): shading rate = 0.25, micropolygonlength = 0.5 |
Displacement Space
We offer two rendering spaces for specifying displacement, world and object space. These are specified in the PxrDispTransform node but explained here.
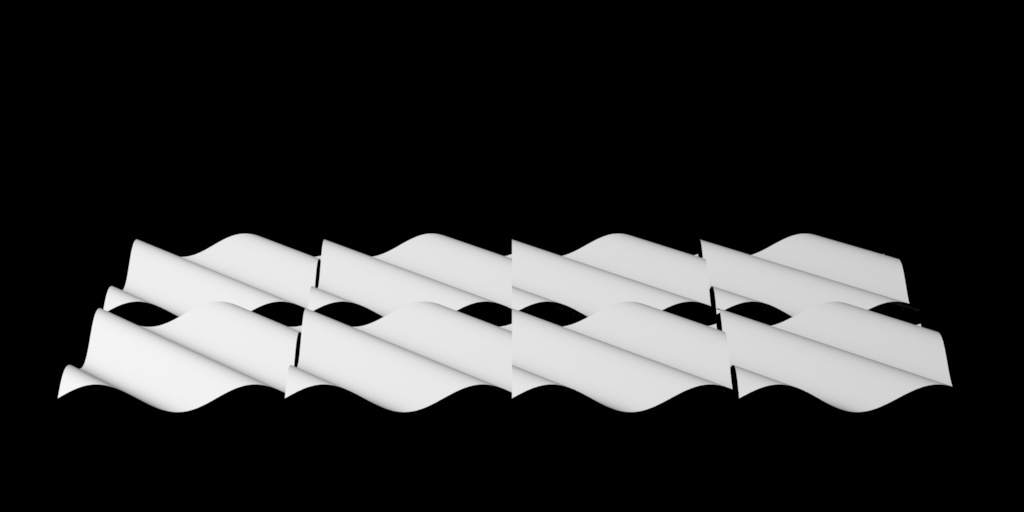
By default, RenderMan will displace in Object space. This is typically desired for sculpted models. But for some objects this can result in discontinuities. For example, a set of objects displaced together like a set of planes made into an environment piece. In object space these may result in gaps or discontinuity between patches like below.
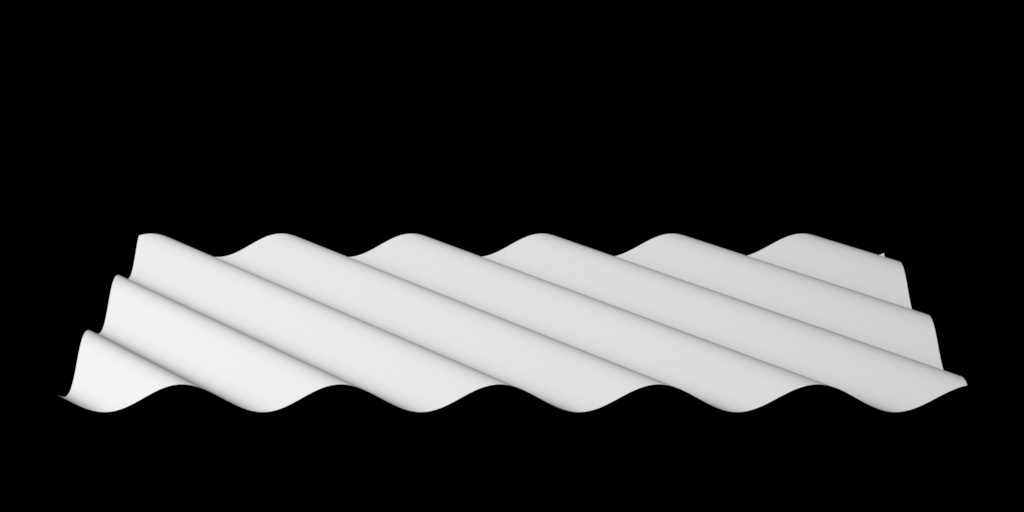
To correct for this particular scenario, you can select World Space to achieve the result below using the same eight patches. This will solve issues like ocean planes, cliffs, and rocks, where displacement is shared across the shapes.
Displacement Types
There are two types of displacement, scalar and vector: The source of both types of displacement can be procedural or textured.
...
| Carousel Image Slider | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hints on performance:
When displacing objects, RenderMan uses a screen projection to dice objects finely into micropolygons. This typically needs no user adjustment and handles level of detail automatically as objects further away are covered by fewer pixels and diced more coarsely.
There are two ways to adjust this should it not meet your requirements.
...
Should you need better quality from the render camera (at the correct location for your final frame) you may decrease the size of the polygons by
...
using Micropolygon Length and reducing this number slowly (decreasing the size of the resulting polygons for finer details).
Always use the smallest bounding box setting that produces the correct and full displacement.