...
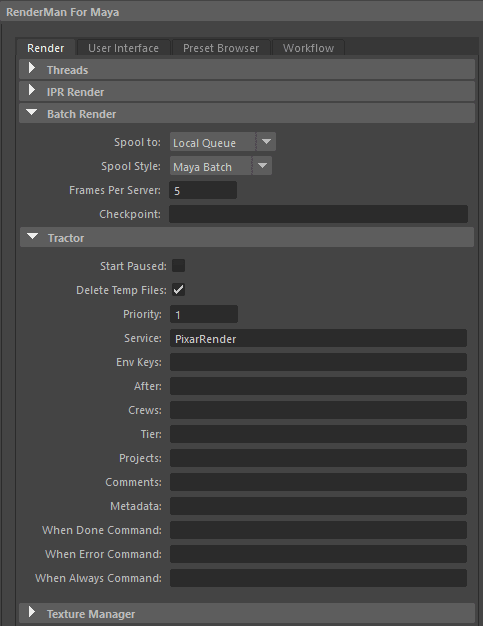
Batch renders are always spooled to either LocalQueue (default) or Tractor. Batch queuing preferences are available in the Maya Preferences window, which opens when you choose the option box for the Batch Render menu item.
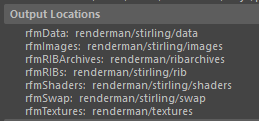
Output Locations
By default, we use Mayabatch to render the saved Maya scene file. Maya renders from memory similarly to a preview render from the UI, without the intermediate RIB export.
When a batch render is started, RIB files and textures are stored on disk and the renderer reads those in. These are stored in a directory based on the scene name but with a time stamp appended. The Batch Context setting in the preferences is where the time stamp is specified as a variable called $JOBDATETIME. This avoids the possibility of multiple simultaneous jobs attempting to overwrite files.
Output locations are configured in RenderMan for Maya's RMSWorkspace.ini initialization file. You can preview the output locations for the current scene under the Workspace tab in the Render Settings. These locations are below the current maya project directory. Note, the time stamp doesn't appear in the preview of the output locations. However, these are the exact locations used for spooled preview renders of the scene.
Local Queue
LocalQueue is used to run a local queue of render jobs. It reads job scripts that are generated by RenderMan for Maya, and then runs the commands from the scripts to render your scene on the local computer.
...
Once a render job is loaded in LocalQueue, you should see it listed in the Jobs table. You can right-click a job to bring up a menu with various options for managing the job. Once you select a job, its commands will be displayed in the Job Commands table.
Rendering Environment
In the RenderMan Preferences an Environment Key can be specified to cause a particular set of environment variables to be used for your render job. This setting has a default value which causes canonical locations of RenderMan and RenderMan for Maya installations to be used. If it is left blank LocalQueue runs commands in the same environment that it was started in.
Checkpointing
By default checkpointing is enabled for batch renders. Images are updated on disk every five minutes. The checkpoint interval is configurable in the batch preferences. Incremental mode is enabled by default, under the Sampling tab in the Render Settings. This is necessary for checkpointing to work.
Maya Batch Rendering from the Command Line
You may also use additional flags: -rl (render layer), -crop, -preRender, -postRender, -preLayer, -postLayer, -preFrame, -postFrame, -jobid
From a command line use the following:
Render -r rmanrenderman sceneFile
It is also possible to only generate RIB without subsequently rendering.
Render -r renderman -rib sceneFile
A complete list of the options can also be seen by running:
Render -r rmanrenderman -h
If you get a warning like the following, you need to put rmanRenderer.xml and ribRenderer.xml from the RenderMan for Maya installation in a place where Maya can find it.
Cannot open renderer description file "rmanRendererrendermanRenderer.xml"
You can copy the files from the RenderMan for Maya installation,
eg. C:/Program Files/Pixar/RenderManForMaya-2122.0-maya2016/etc/rmanRendererrendermanRenderer.xml
Into the directory where Maya looks for these under the Maya installation,
eg. C:/Program Files/Autodesk/Maya2016Maya2018/bin/rendererDesc/
Or you can set up the Maya environment variable called MAYA_RENDER_DESC_PATH so that rmanRenderer.xml and ribRenderer.xml will be found.
Prman Rendering from the Command Line (Advanced)
When doing a maya batch render, RenderMan for Maya generates RIB files and then prman (executable) is launched for those rib files. However, you may already have RIB files on disk and just want to run prman on them.
...
renderman/test_0725120019/rib/0001:
0001.ribdeformingGeoCache.0001.zipperspShape_Final.0001.rib
...
There are some files in the directory that aren't RIB files. What are those?
The RLF file contains user made RLF files (assigned for GPU archives) contain material and binding information. Materials are injected into the RIB file by a RIF at render time.
The XML file is generated during rendering. It contains diagnostic information about the render.The file called deformingGeoCache.0001.zip contains rib files for deforming pieces of geometry. The rib file for a pass, like perspShape_Final.0001.rib references geometry from cache files, either the frame specific cache of deforming objects or the job cache for static objects.
Flattening RIB
You may want to distill a render pass down to a single file. For example, if you want to give it to another person, without having to package up a directory. Here are some steps for generating a flattened RIB file using RenderMan for Maya.
- Embed geometry in RIB for each pass. In the Render Settings, under the Advanced tab, find the RIB Options section, and enable "Flatten".
- Embed shading information in RIB by disabling RLF. In the mel script window type: rman setPref DisableRifShadingAttachment 1
Textures will still be referenced externally. RIB files are also still generated per pass.
To generate the flattened RIB, kick off a render from Maya as you normally would.
There is also a mel command that will just generate rib, as if for a batch render: rman genrib;