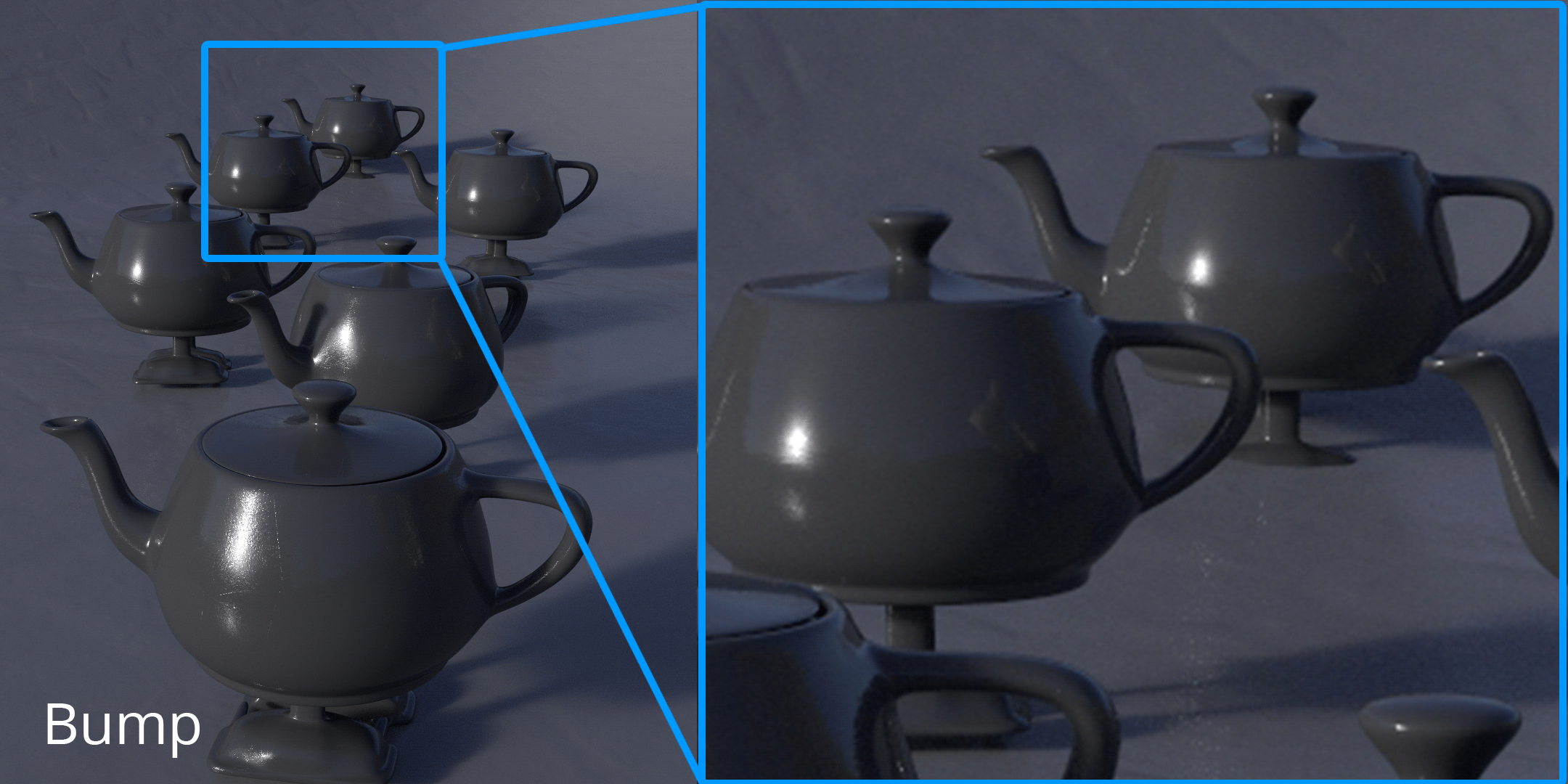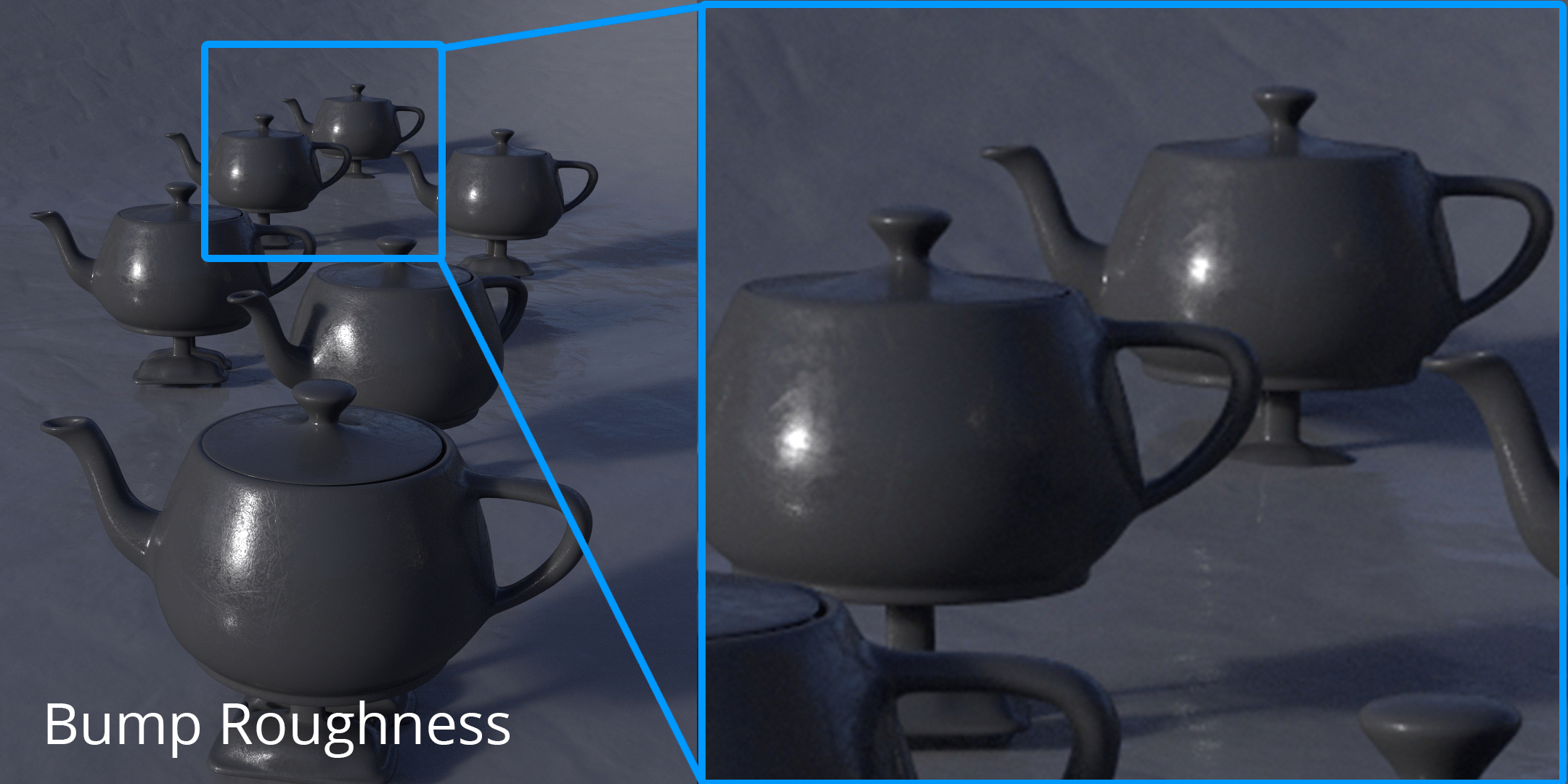
Bump Roughness was created for efficiently sampling micro details. With this pattern, RenderMan automatically switches from a bump map to a roughness value depending on the size of a feature in the camera, effectively improving your render times by lowering the sampling rates needed to render such details.
© Disney/ Pixar
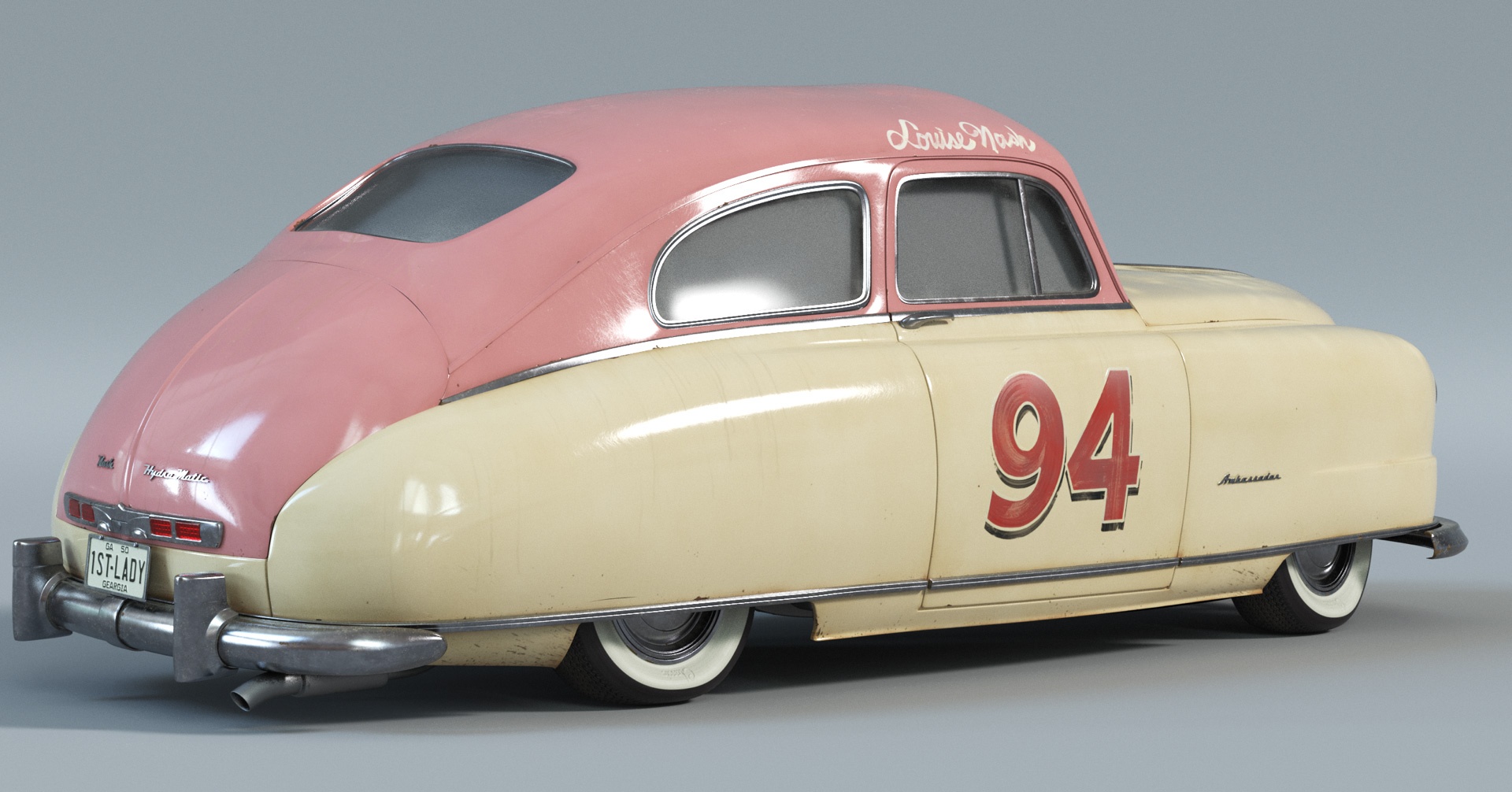
One such example is Louise Nash (shaded by Yeon Kang) from Cars 3. Here you can see extensive wear of the clear coat on the paint job, which creates micro-scratches and breaks up the specular in interesting ways, also driving the anisotropy in ways which more accurately reflect the intended look-development.
© Disney/ Pixar
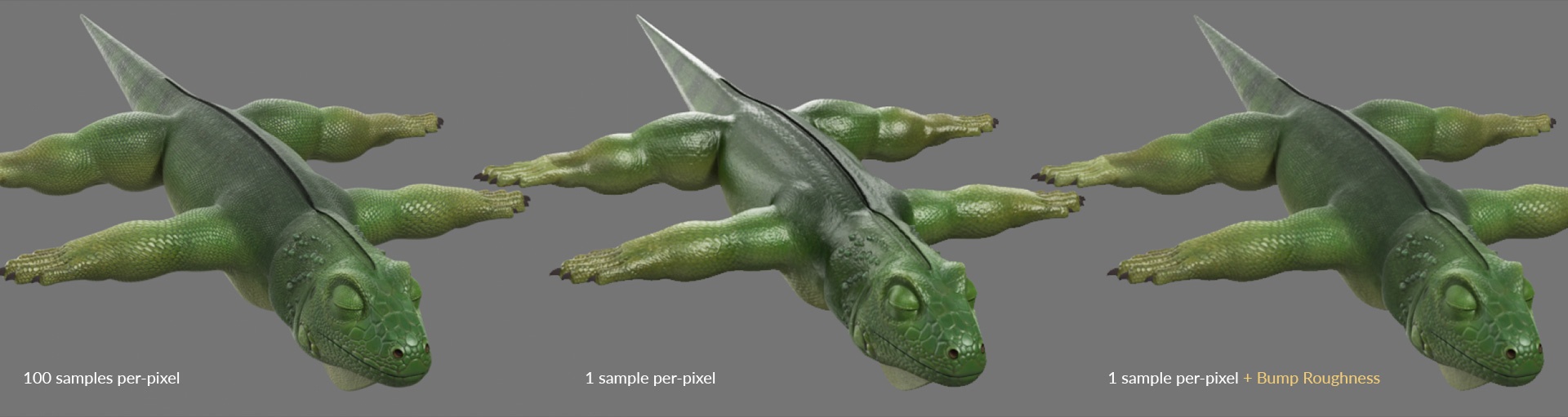
A crucial feature
...
of Bump Roughness
...
is to see micro details when objects are far from the camera. In the example above, you can see how we can get very close to the intended look-development with only 1 sample, instead of having to fire hundreds of rays to visualize the intended level of detail in the textures.
In the example above we can see how we can drive roughness, anisotropy, and bump with a single texture. When zooming 4X we can appreciate how Bump Roughness maintains detail where bump generally gets lost due to filtering.
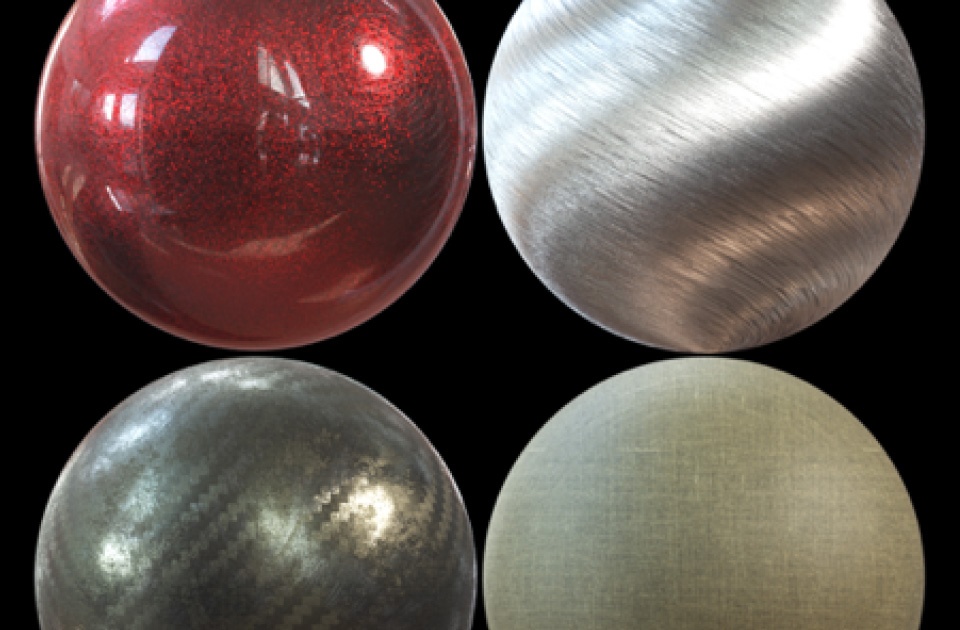
There are many other types of materials that benefit from the added detail that Bump Roughness maps bring, such as carbon fibre, metals, plastics, and fabrics.
© Disney/ Pixar
...
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
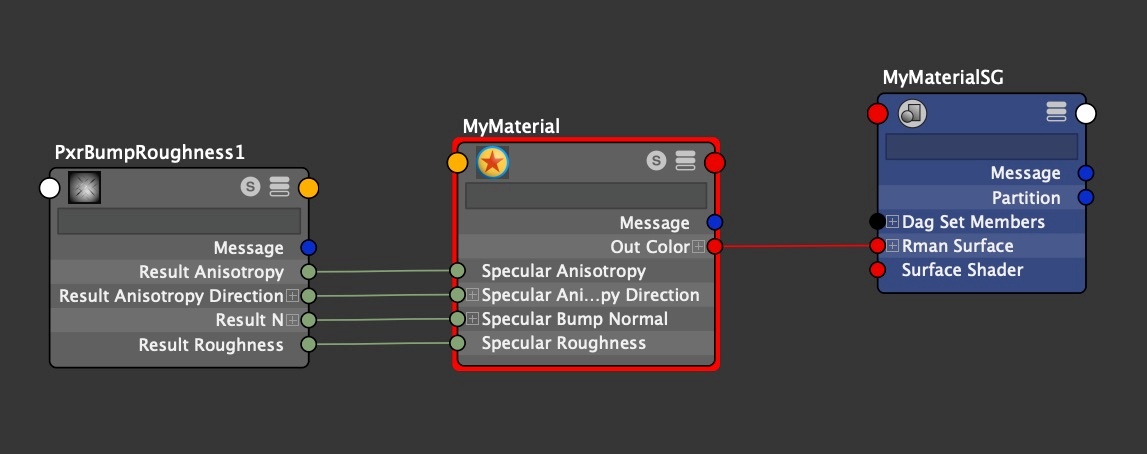
For Bump Roughness to work appropriately, it needs to be connected to |
...
the following material inputs:
|
Input Parameters
b2r Texture
Simply use traditional bump or normal maps and the Texture Manager will convert them to Bump Roughness textures automatically in RFM, RFH or RFB. You'll notice your newly created tex files now have a b2r suffix after the file name, such as myTexture_b2r.exr.tex
See the txmake documentation for details.This expects the first derivative map, let H be a height field, then each channel are defined as r=dH/du, g=dH/dv, b=dontcare
Texture Type
Map type to be used as your Bump Roughness Map
...