This Bxdf is based on Brent Burley's extended material model, introduced in "Extending the Disney BRDF to a BSDF with Integrated Subsurface Scattering" at SIGGRAPH 2015.
The PxrDisneyBsdf is a nice and straightforward physically-based model with a concise number of parameters, allowing for a wide range of photoreal and artistic materials, including diffuse and specular reflection and transmission, clearcoat, sheen, and subsurface scattering.
All CG animations made at Walt Disney Animation Studios use this material model and the source code for the Pixar version of this material, PxrDisneyBsdf, is available among the bxdf code examples.
Examples of different material parameter settings for PxrDisneyBsdf: metallic reflection, thin diffuse transmission, thin specular transmission, subsurface scattering, and glass refraction and reflection. Image inspired by Figure 1 of the Burley Bsdf paper.
...
Basic
Base Color
The main surface color, usually supplied by texture maps.
Emit Color
The The emission energy. Non-black values represent glow. Use this parameter with care. Only use for low emission objects and materials. For brighter objects, always use a PxrMeshLight.
Specular Reflection
Metallic
The Defines the metallic-ness (0=of your material. 0 is a dielectric, 1=metallic). whereas a value of 1 is fully metallic. A PBR Metalness map can be used as the input.
This is a linear blend between two different models. The metallic model has no diffuse component and also has a tinted incident specular equal to the base color.
...
A concession for artistic control that tints incident specular towards the base color. Grazing specular is still achromatic (i.e. it doesn't tint incoming light).
Roughness
Surface roughness controls both Defines the surface roughness between the diffuse and specular responses. Again, usually, a PBR Roughness map would be used as the input to add roughness variation.
Anisotropic
The degree of anisotropy , controls the aspect ratio of the specular highlight. 0: isotropic, 1: maximally anisotropic.
...
The index of refraction of the material which controls , controlling refraction, and also the amount of specular reflection. (It also influences subsurface scattering.)
...
Controls the intensity of specular reflection; 0. 0 removes it and 1 .0 maintains the full specular reflection response. This parameter is usually not needed as the specular response is determined by the incident angle of light and the roughness and IOR parameters in a physically correct way, but this parameter can override that.
...
An additional grazing angle / forward scatter diffuse component, primarily intended for cloth.cloth
Sheen Tint
Amount of tint sheen toward base color. At 0, the sheen is achromatic (i.e. doesn't tint incoming light).
...
Whether the surface should be considered thin or that it forms the interface to a thick material. When set to Thin, the index of refraction is 1.0
Transmission Color
The color of transmitted light for volumetric absorption (Beer's exponential extinction law).
...
Subsurface volume anisotropy (mean cosine for scattering) in path-traced subsurface scattering. 0 means isotropic scattering, values between 0 and 1 means mainly forward scattering, values between -1 and 0 means mainly backscattering.
Other parameters
Transmission Behavior
Select a transmission behavior for shadow rays: opaque or use baseColor.
...
Connect a mask function here to apply a cutout pattern to your object. Presence is defined as a binary (0 or 1) function that can take on continuous values to antialias the
shape. Useful for modeling leaves and other thin, complex shapes.
...
Input AOV
Plug a MatteID node here.
...
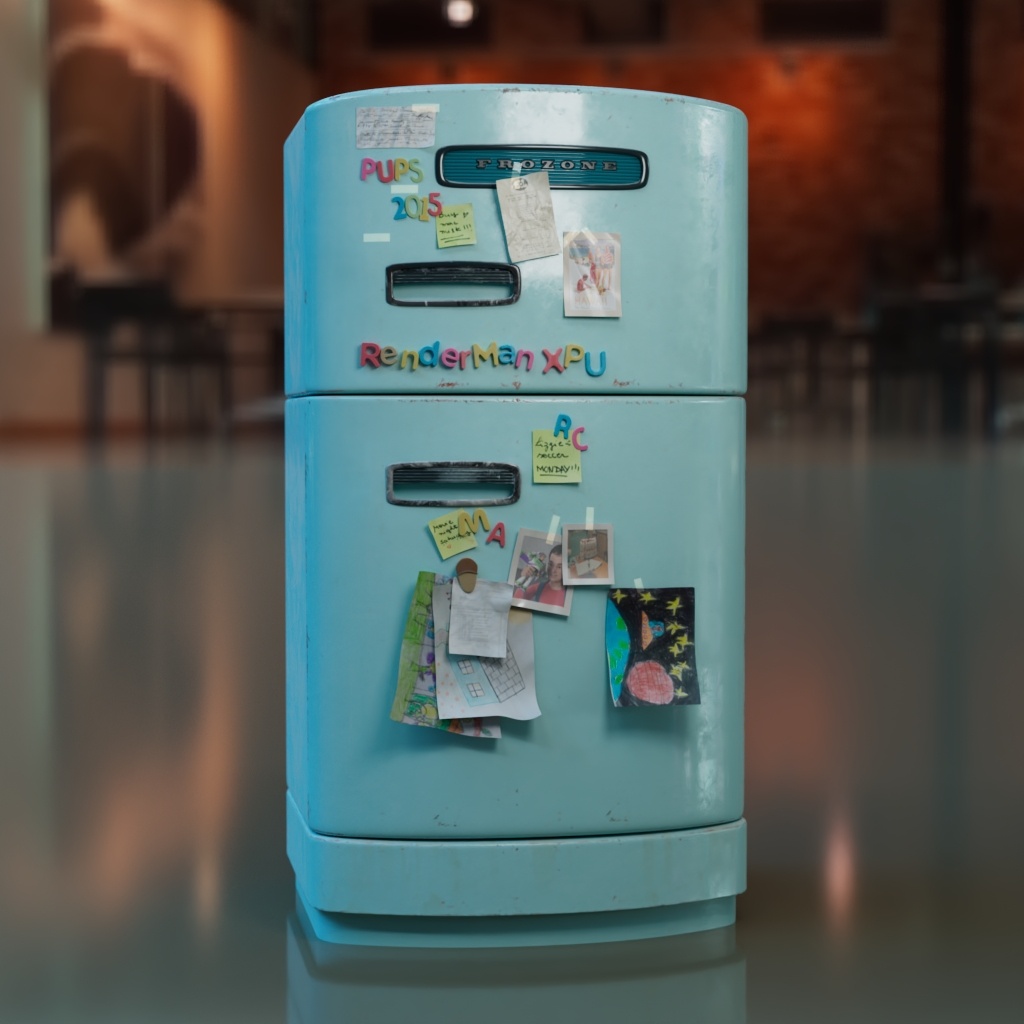
PxrDisney Fridge
You can download this PxrDisney example here
Fridge was created by artist Fabio Sciedlarczyk.