A RixShadingContext encapsulates a shading context - a description of the environment in which shading is to be performed. It is the primary domain of operation for the shader classes
RixBxdf
,
RixDisplacement
,
RixLight
,
RixPattern
, and
RixVolume
, and is also of high importance to
RixIntegrator
. Implementors of these classes and their associated plugins will thus need to be intimately familiar with the RixShadingContext class.
A RixShadingContext usually represents a collection of one or more geometric points that may be shaded. The group of points may arrive via ray tracing hits on geometry, or may be associated with tessellated micropolygons. In either case, shaders will make use of the shading context primarily in one of two ways: inquiring about geometric information through the GetPrimVar() and GetBuiltinVar() methods, and evaluation of the input parameters to the shading function is provided via the EvalParam() methods.
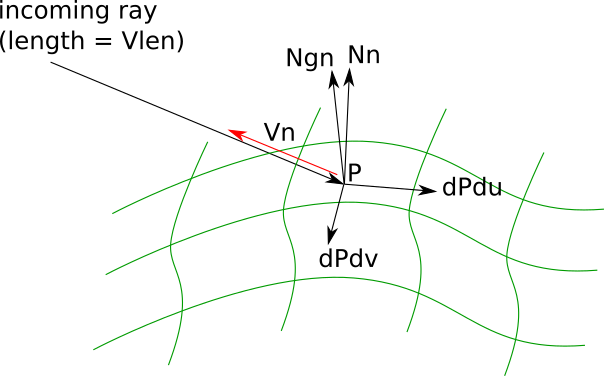
Builtin variables represent values which are usually always present for all geometry types, and are often used in fundamental shader calculations. Some variables like P, the shading position, and Nn, the normalized shading normal, are derived from the geometry definition. Others like incidentRaySpread and VLen are derived from the incoming rays or from a combination of the geometry definition and the incoming rays.
RtFloat3 P: The position of the point being shaded. Derived directly from the underlying tessellated representation used during hit testing.float PRadius: When the geometry is a collection of hits, the radius of the incident ray at P. Otherwise it is half the micropolygon radius at P.RtFloat3 Po: If the geometry was displaced, the value of the undisplaced position that became P after displacementRtFloat3 Nn: The normalized shading normal, which is the normal that is typically used for shading because it has the smoothest appearance in all circumstances.RtFloat3 Ngn: The normalized geometric normal. The geometric normal is the normal derived directly from the underlying tessellated representation used during hit testing, and may be preferred to the shading normal for certain uses such as horizon culling.RtFloat3 Non: The normalized undisplaced normal, i.e. equivalent to Nn if the geometry did not undergo displacement.RtFloat3 Tn: The shading tangent. Typically a vector which is orthonormal to the shading normal Nn, often used in conjunction with same to create an orthonormal basis.RtFloat3 Vn: The normalized view vector, pointing away from P. In ray tracing contexts, this is the reverse direction of the incoming ray. In other contexts where there is no view direction, this may be set to the same as Nn.float VLen: The length of the view vector.float curvature: The local mean surface curvature, which is the average of curvatureU and curvatureV.float incidentRaySpread: How much the ray radius increases for each unit distance the incident travels.float incidentRayRadius: Radius of incident ray at P.int incidentLobeSampled: RixBXLobeSampled id of incident rays.float mpSize: The micropolygon size. 0 for non-tessellated surfaces. May be used as a hint for biasing purposes.float biasR: A renderer-computed bias used for reflected rays.float biasT: A renderer-computed bias used for transmitted rays.float u: The position of the current point on the current surface in parametric space.float v: The position of the current point on the current surface in parametric space.float w: The position of the current point on the current surface in parametric space.float du: The size of the ray footprint (radius) in parametric space.float dv: The size of the ray footprint (radius) in parametric space.float dw: The size of the ray footprint (radius) in parametric space.RtFloat3 dPdu: The surface derivative of P with respect to u.RtFloat3 dPdv: The surface derivative of P with respect to v.RtFloat3 dPdw: The surface derivative of P with respect to w.RtFloat3 dPdtime: The instantaneous velocity of P in current space.float time: The shading time of the point being shaded, normalized between shutter open and shutter close.int Id: The value of any Attribute "identifier" "id" associated with the geometry.int Id2: The value of any Attribute "identifier" "id2" associated with the geometry.float outsideIOR: The incident index of refraction.RtFloat3 Oi: The opacity.RixLPEState lpeState: The current LPE state.int launchShadingCtxId: The ID of the shading context that launched the incident ray.RtFloat3 motionFore: Forward 2D raster-space motion vector.RtFloat3 motionBack: Backwards 2D raster-space motion vector.float curvatureU: The principal curvature in the parametric u direction, computed via dot(dNu, dPu) / |dPu|^2, where dNu is a difference between two surface normals computed at P and P' (P' being a point near P offset in the u direction) and dPu is the difference between P and P`. This is a signed quantity. float curvatureV: The principal curvature in the parametric v direction, computed via dot(dNv, dPv) / |dPv|^2, where dNv is a difference between two surface normals computed at P and P' (P' being a point near P offset in the v direction) and dPv is the difference between P and P`. This is a signed quantity. RtFloat3 dPcameradtime: The instantaneous velocity of P relative to the camera.float wavelength: The wavelength of the incident ray.The following diagram illustrates several fundamental geometric properties: the surface position P, the normalized shading normal Nn, and the parametric derivatives dPdu and dPdv, as well as Vlen and Vn which provide information about the incoming ray.

Primitive Variables
Primitive variables (often referred to as primvars) represent values which are optionally present on the geometry. They may be supplied with the geometry definition.
Associated with each primvar is a varying filter size that is computed as a function of rendering conditions such as shading rate and ray differentials. The incoming positions are not guaranteed to be neighbors and so do not support requirements for computing first-differences. Rather, differential information is embodied through filter radii and these are only computable for known builtin and primitive variables.
shadingCtxTraits conveys a variety of (uniform) ShadingContext traits to shader and integrator.
Allocate is fast memory allocation support from a memory pool tailored to Pattern and Bxdf plugins. Memory allocated via this interface is managed (freed) by RixShadingContext according to the lifetime requirements of the associated MemCategory. As with many custom memory allocation schemes, clients should use "placement new" and not rely on invocation of a destructor. RixAlloca can be used for intra-procedure dynamic memory allocation.
Document New, Allocator etc
Parameter Evaluation
; any such parameters that are connections may trigger the evaluation of upstream nodes.