...
In Auto mode, Fresnel Blend will be used when the base layer is diffuse, while Rough Coating will be used when the base layer is specular.
Layering Modes
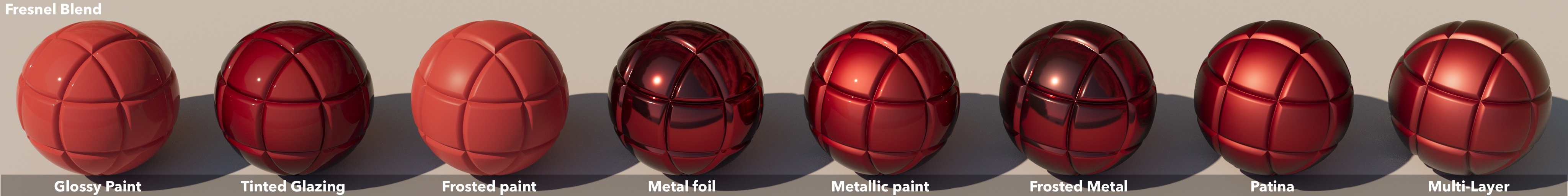
Fresnel Blend
| Section | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
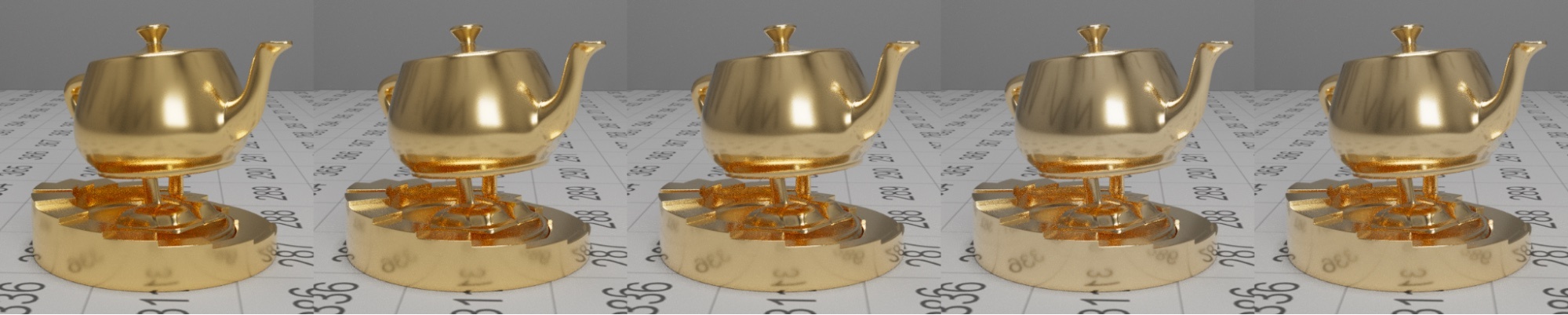
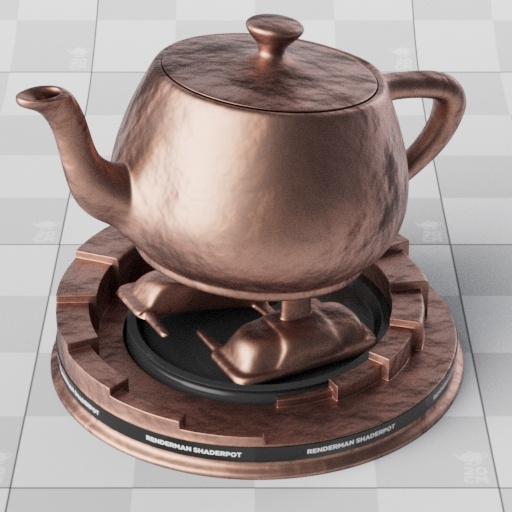
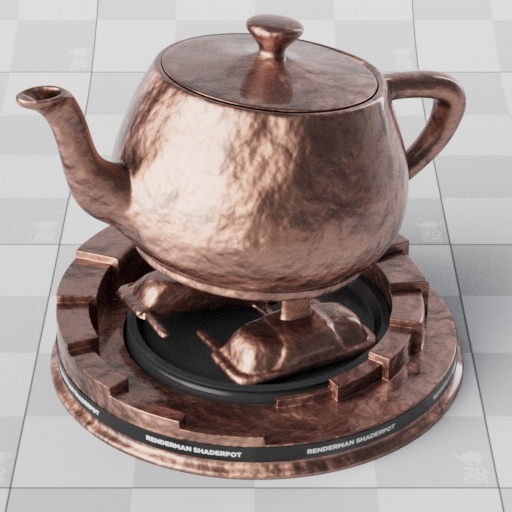
| Rough gold base layer and dielectric top layer with varying IOR (1.0-3.0) |
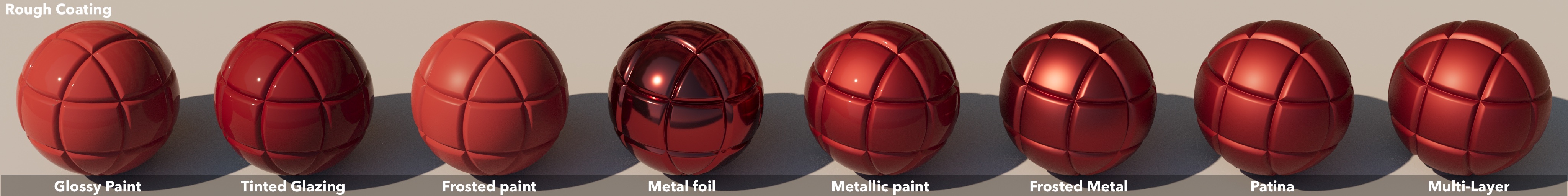
Rough Coating
| Section | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
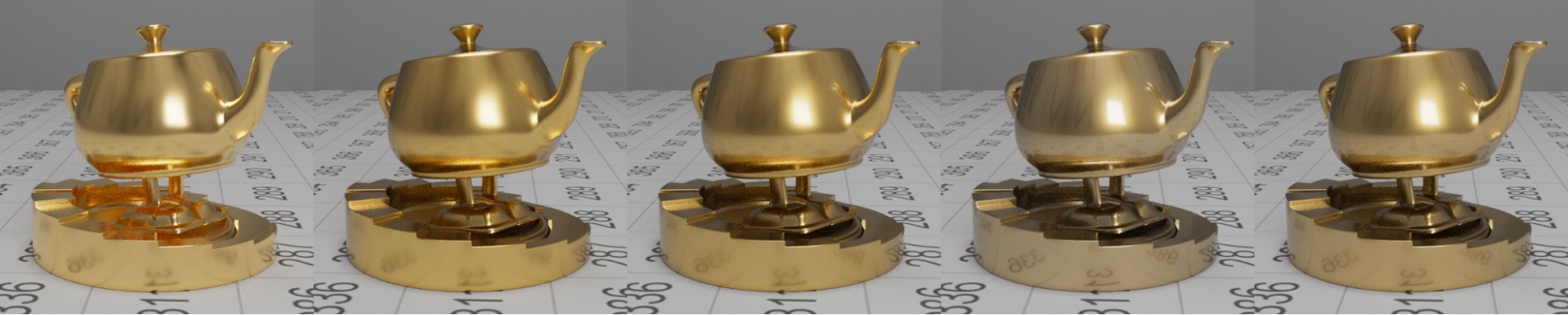
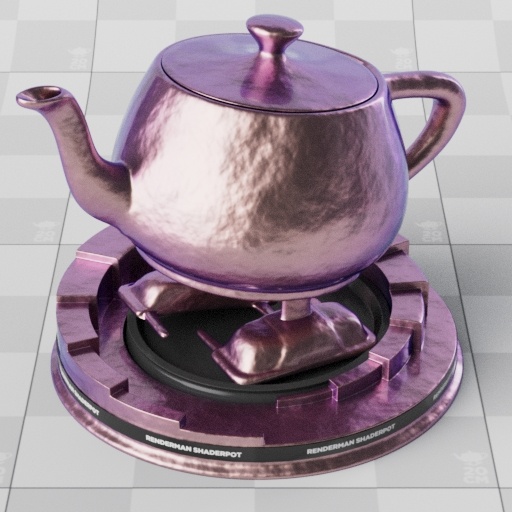
| Rough gold base layer and dielectric top layer with varying IOR (1.0-3.0) |
Attenuation
| LamaDielectric (absorptionColor set to red) layered on top of a white LamaDiffuse, layer thickness varying from 1 to 3.2 |
The top layer is considered for both the outgoing and incoming rays, meaning that the ray is attenuated by the top layer twice: once when it leaves and once when it exits. This is the case for both fresnel attenuation at the interface, and for absorption through the thickness of the layer.
...
The IOR of the top layer is also tracked, so that the relative IOR of the base layer is correct. For example, if there is a water layer on top of a skin layer, the relative IOR of the skin layer will be reduced, causing lower reflectivity.
Smooth Coating
The smooth coating layer mode is very similar to the rough coating mode, but without the roughness clamping. This allows for greater control of the base layer roughness.
Auto
The auto mode is identical to rough coating in most cases, but switches to fresnel blend for diffuse layers. This is to accommodate for the common Diffuse < Specular < Clearcoat material configuration, where the diffuse and specular materials are thought of as one single base material, with the clearcoat sitting on top.
Comparisons
Weidlich & Wilkie surface types
These images show a collection of simple and common material configurations, inspired by Weidlich and Wilkie's arbitrarily layered micro-facet surfaces . These have been rendered with both the fresnel blend mode, and rough coating mode.
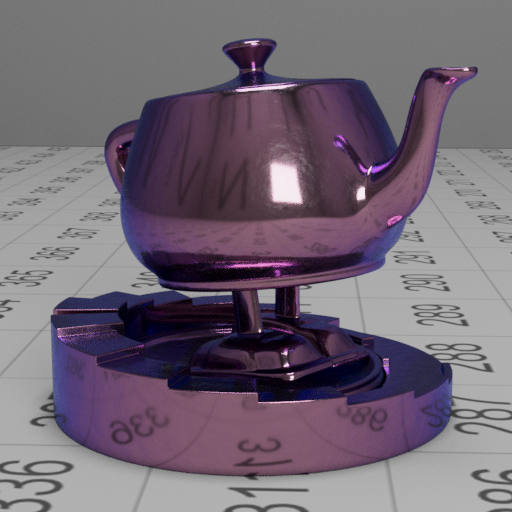
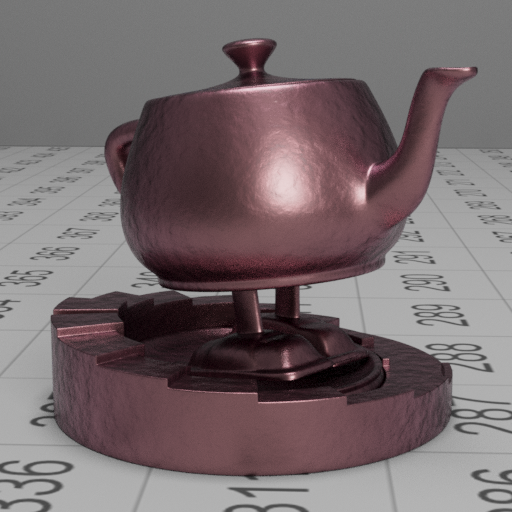
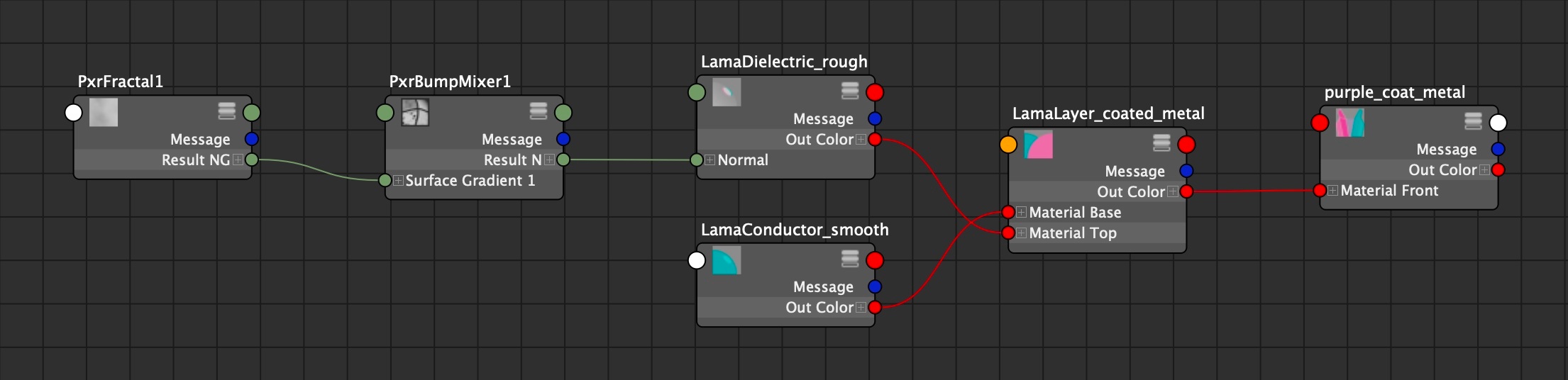
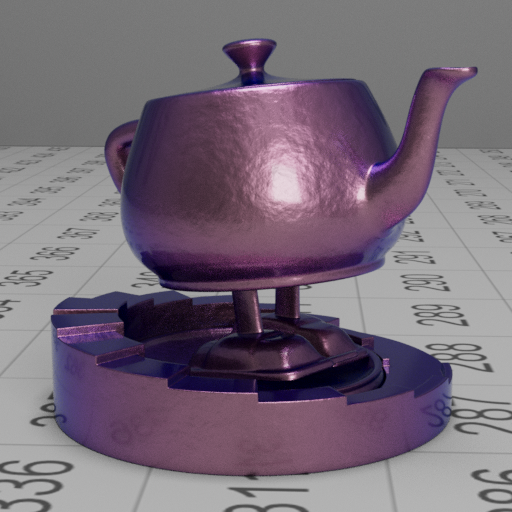
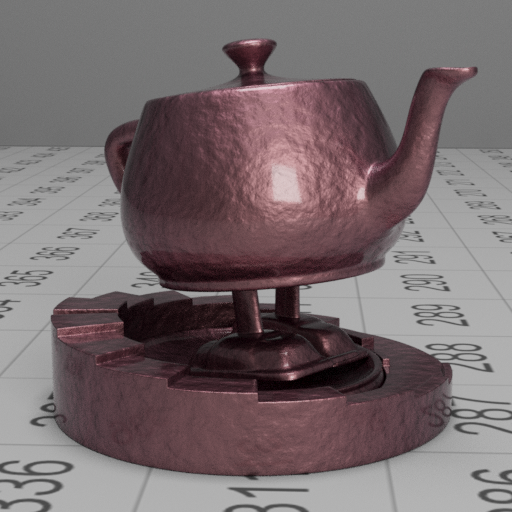
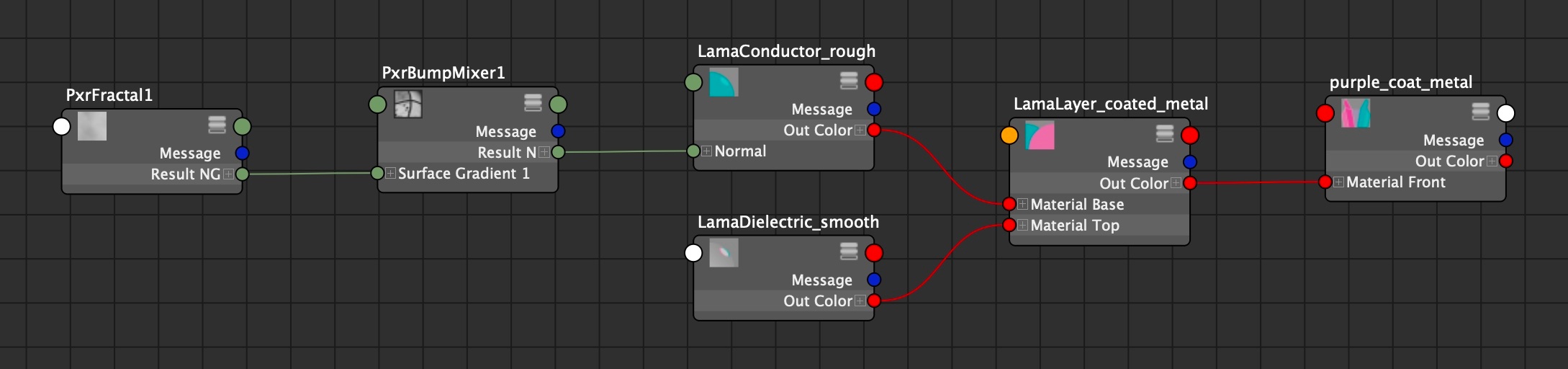
Smooth gold with a rough/bumpy purple coating
These images show a smooth gold base layer with a bump mapped dielectric with absorption.
...
We can also see that in the rough coating image, the base layer reflection is much more diffused, this is due to the scattering of rays through the top layer, which is achieved by the roughness approximation.
| fresnel blend | rough coating |
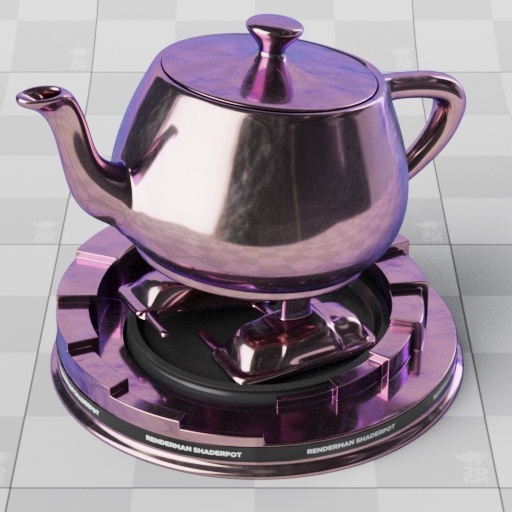
Rough/bumpy gold with a smooth purple coating
These images are of a similar material configuration, but with the roughness and bump map on the base layer instead of the top layer. This configuration demonstrates that even when the top layer is smooth, it still creates a difference in look due to the refraction and compression of rays that reach the base layer.
fresnel blend | rough coating |